Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019
Sep 20, 2010 If you frequently access a file server from a Mac it’s pretty helpful to map the network drive to your desktop. There’s two ways to do this, one method is just mapped for one time use and will reset after a reboot, and another method is a more permanent route that allows the mapped network drive to always appear and mount on your desktop after system reboots and user logins. Aug 01, 2001 Mac OS X System & Mac Software. Change File Mapping. Thread starter Wowzer; Start date May 29, 2001; W. Wowzer Registered. May 29, 2001 #1 Is there any way to change the File Mapping in OSX? Is there any way to change the File Mapping in OSX? Its annoying to launch Classic just because of a SimpleText document. There must be an easy way to.
- Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Download
- Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Mac
- Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Online
- Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Free
Disk Utility User Guide
Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Download
You can use Disk Utility to create a disk image, which is a file that contains other files and folders.
Note: You can burn information to a CD or DVD using the Burn command in the Finder. See Burn CDs and DVDs.

Create a blank disk image for storage
You can create an empty disk image, add data to it, then use it to create disks, CDs, or DVDs.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File > New Image > Blank Image.
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
In the Name field, enter the name for the disk image.
This is the name that appears on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar, after you open the disk image.
In the Size field, enter a size for the disk image.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose the format for the disk:
If the disk image will be used with a Mac that has a solid state drive (SSD) and uses macOS 10.13 or later, choose APFS or APFS (Case-sensitive).
If the disk image will be used with a Mac with macOS 10.12 or earlier, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled) or Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled).
If the disk image will be used with a Mac or Windows computer and is 32 GB or less, choose MS-DOS (FAT); if it’s over 32 GB, choose ExFAT.
To encrypt the disk image, click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Click the Partitions pop-up menu, then choose a partition layout.
Click the Image Format pop-up menu, then choose an option:
Sparse bundle disk image: Same as a sparse disk image (below), but the directory data for the image is stored differently. Uses the .sparsebundle file extension.
Sparse disk image: Creates an expandable file that shrinks and grows as needed. No additional space is used. Uses the .sparseimage file extension.
Read/write disk image: Allows you to add files to the disk image after it’s created. Uses the .dmg file extension.
DVD/CD master: Changes the size of the image to 177 MB (CD 8 cm). Uses the .cdr file extension.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
In the Finder, copy your files to the mounted disk image, then eject it.
Restore the disk image to a disk.
For more information about disk image types, see the manual (man) page for hdiutil.
Create a disk image from a disk or connected device
You can create a disk image that includes the data and free space on a physical disk or connected device, such as a USB device. For example, if a USB device or volume is 80 GB with 10 GB of data, the disk image will be 80 GB in size and include data and free space. You can then restore that disk image to another volume.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, select a disk, volume, or connected device in the sidebar.
Choose File > New Image, then choose “Image from [device name].”
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose an option:
Read-only: The disk image can’t be written to, and is quicker to create and open.
Compressed: Compresses data, so the disk image is smaller than the original data. The disk image is read-only.
Read/write: Allows you to add files to the disk image after it’s created.
DVD/CD master: Can be used with third-party apps. It includes a copy of all sectors of the disk image, whether they’re used or not. When you use a master disk image to create other DVDs or CDs, all data is copied exactly.
To encrypt the disk image, click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
Important: Don’t create a disk image of a disk that you believe to be failing or that contains corrupted information. The disk image may not serve as a reliable backup.
For technical information about creating a restore disk image, see the Apple Software Restore (ASR) manual (man) page.
Create a disk image from a folder or connected device
You can create a disk image that contains the contents of a folder or connected device, such as a USB device. This method doesn’t copy a device’s free space to the disk image. For example, if a USB device or volume is 80 GB with 10 GB of data, the disk image will be 10 GB in size and include only data, not free space. You can then restore that disk image to another volume.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File > New Image, then choose Image from Folder.
Select the folder or connected device in the dialog that appears, then click Open.
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
To encrypt the disk image, click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Click the Image Format pop-up menu, then choose an option:
Read-only: The disk image can’t be written to, and is quicker to create and open.
Compressed: Compresses data, so the disk image is smaller than the original data. The disk image is read-only.
Read/write: Allows you to add files to the disk image after it’s created.
DVD/CD master: Can be used with third-party apps. It includes a copy of all sectors of the disk image, whether they’re used or not. When you use a master disk image to create other DVDs or CDs, all data is copied exactly.
Hybrid image (HFS+/ISO/UDF): This disk image is a combination of disk image formats and can be used with different file system standards, such as HFS, ISO, and UDF.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
For technical information about creating a restore disk image, see the Apple Software Restore (ASR) manual (man) page.
Create a secure disk image
If you have confidential documents that you don’t want others to see without your permission, you can put them in an encrypted disk image.
Note: If you want to protect the contents of the system disk, turn on FileVault using the FileVault pane of Security & Privacy Preferences.
In the Disk Utility app on your Mac, choose File > New Image > Blank Image.
Enter a filename for the disk image, add tags if necessary, then choose where to save it.
This is the name that appears in the Finder, where you save the disk image file before opening it.
In the Name field, enter the name for the disk image.
This is the name that appears on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar, after you open the disk image.
In the Size field, enter a size for the disk image.
Click the Format pop-up menu, then choose a format:
If you’re using the encrypted disk image with a Mac computer using macOS 10.13 or later, choose APFS or APFS (Case-sensitive).
If you’re using the encrypted disk image with a Mac computer using macOS 10.12 or earlier, choose Mac OS Extended (Journaled) or Mac OS Extended (Case-sensitive, Journaled).
Click the Encryption pop-up menu, then choose an encryption option.
Enter and re-enter a password to unlock the disk image, then click Choose.
WARNING: If you forget this password, you won’t be able to open the disk image and view any of the files.
Use the default settings for the rest of the options:
Click the Partitions pop-up menu, then choose Single partition - GUID Partition Map.
Click the Image Format pop-up menu, then choose “read/write” disk image.
Click Save, then click Done.
Disk Utility creates the disk image file where you saved it in the Finder and mounts its disk icon on your desktop and in the Finder sidebar.
In the Finder , copy the documents you want to protect to the disk image.
If you want to erase the original documents so they can’t be recovered, drag them to the Trash, then choose Finder > Empty Trash.
When you’re finished using the documents on the secure disk image, be sure to eject the disk image. As long as it’s available on your desktop, anyone with access to your computer can use the documents on it.
To access the data in a disk image, double-click it. It appears on your desktop, and you can add, remove, and edit files on it just as you would with a disk.
Look at the folder structure of a typical OS X installation. Open a Finder window and click the icon for your hard drive (which is typically called Macintosh HD) in the Sidebar. You should see at least four folders: Applications, Library, System, and Users. Within the Users folder, each user has his own set of folders containing documents, preferences, and other information that belongs to that user and account.
From the top: The Computer folder
The Computer folder shows all the storage devices that are currently connected to your Mac. The following steps show how you can start at the Computer folder and drill down through the folder structure:
To find the Computer folder, choose Go→Computer or press Shift+Command+C.
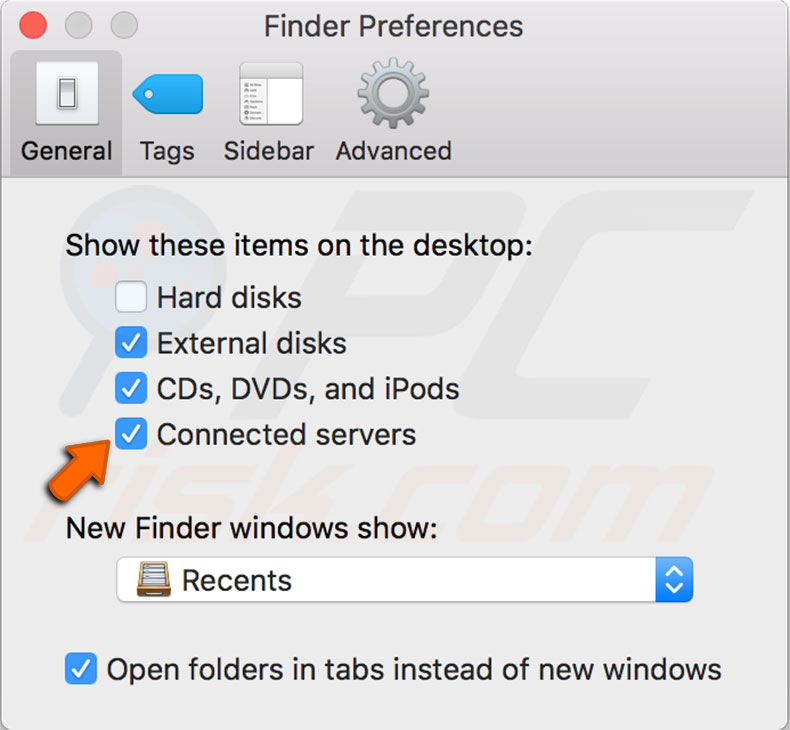
The Computer folder in this example is called Bob L’s MacBook Pro, and it contains a hard-drive icon (Mavericks HD) and a Network icon, with which you can access servers or other computers on your local network.
Double-click the icon that holds your OS X stuff.
Technically, this drive is called your boot drive. If you haven’t changed it, it’s probably called Macintosh HD.
Check out the folders you find there.
You should see at least four folders (unless you’ve added some; if you installed the Xcode programming tools, for example, you have more).
The Applications folder
You can access the Applications folder, located at the root level of your boot drive, by clicking the Applications icon in the Sidebar, by choosing it in the Go menu, or by pressing Shift+Command+A. In this folder, you find applications and utilities that Apple includes with OS X.
Fonts (and more) in the public Library folder
The Library folder, at the root level of your OS X hard drive, is like a public library; it stores items available to everyone who logs into any account on this Mac.
Leave the /System/Library folder alone.Don’t move, remove, or rename it, or do anything within it. It’s the nerve center of your Mac. In other words, you should never have to touch this third Library folder.
By and large, the public Library subfolder that gets the most use is the Fonts folder, which houses many of the fonts installed on the Mac
Finally, the Library in the Users folder is where OS X stores configuration and preferences files shared by all users.
If your Mac is set up for multiple users, only users with administrator (admin) privileges can put stuff in the public (root-level) Library folder.
You can upgrade to a later version afterward. And Shift-Option-Command-R isn't available. If you instead of just the startup volume on that disk, macOS Recovery might offer only the macOS that came with your Mac, or the closest version still available. How to install mac os on a external hard drive.
The System folder
The System folder contains the files that OS X needs to start up and keep working.
Leave the System folder alone.Don’t move, remove, or rename it or anything within it. It’s part of the nerve center of your Mac.
The usability of the Users folder
When you open the Users folder, you see a folder for each person who has a user account on the Mac, as well as the Shared folder.
The Shared folder that you see inside the Users folder allows everyone who uses the Mac to use any files stored there. If you want other people who use your Mac to have access to a file or folder, the Shared folder is the proper place to stash it.
There’s no place like Home
From the Users folder, you can drill down into the Home folder to see what’s inside. When the user logs on to this Mac, his Home folder appears whenever he clicks the Home icon in the Sidebar, chooses Go→Home, or uses the keyboard shortcut Shift+Command+H.
Your Home folder is the most important folder for you as a user — or at least the one where you stash most of your files. It is strongly recommend that you store all the files you create in subfolders within your Home folder — preferably, in subfolders in your Home/Documents folder.
When you open your Home folder, you see a Finder window with a little house icon and your short username in the title bar. Seeing your short username in the title bar tells you that you’re in your Home folder. Every user has a Home folder named after his or her short username.
Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Mac
If your Mac has more than one user, you can see the other users’ Home folders in your Users folder, but OS X prevents you from opening files from or saving files to them.
Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Online
By default, your Home folder has several folders inside it created by OS X. The following four are the most important:
Desktop: If you put items (files, folders, applications, or aliases) on the Desktop, they’re actually stored in the Desktop folder.
Documents: This is the place to put all the documents (letters, spreadsheets, recipes, and novels) that you create.
Library: This Library folder is invisible in Mavericks. Rest assured that even though it’s hidden, it’s still one of the most important folders in your Home folder, containing Preferences, fonts available only to you, and other stuff that you expect to use.
Public: If others on your local area network use file sharing to connect with your Mac, they can’t see or use the files or folders in your Home folder, but they can share files you’ve stored in your Home folder’s Public folder.
Mac Os X Make Permanent Drive Folder Mapping 2019 Free
You can create more folders, if you like. In fact, every folder that you ever create (at least every one you create on this particular hard drive or volume) should be within your Home folder.